Author: admin
Mindfulness and Stress Reduction
Posted on December 27, 2020 by admin
The physical results of stress:
Stress can have a negative impact on our physical health and cause things such as headaches, stiffness, muscle aches, and pains. Additionally, tight muscles can lead to posture issues and poor sleep, which can end up creating more stress.
To avoid stress affecting your physical health, make sure to always adjust your posture especially at times when you are feeling stressed. Having improper posture frequently can lead to problems with your back and spine overtime. If you are clenched up and feeling stressed, check your posture and adjust your posture so that you are sitting up tall and straight. To make sure you are maintaining a straight back position, it is best to sit on a chair with back support or have your back against a wall.
The importance of mindfulness:
Mindfulness meditation is a common technique used to combat stress, anxiety, chronic pain, depression, and headaches. Add mindfulness to your everyday routine; even as little as 10 minutes can make a big difference in our overall sense of well-being. Meditation is easy to implement to anyone’s lifestyle, as it is a cost saving practice that involves low physical and emotional risk and has the potential to empower people to be more actively engaged in their mental health.
Some significant health benefits of mindfulness are insignificant improvements in pain, anxiety, overall well-being, and the ability to participate in daily activities. Incorporating mindfulness frequently has also been found to improve your overall mood and reduce stress.
Ways to practice mindfulness:
Workspace Ergonomics
Posted on December 2, 2020 by admin
What is Ergonomics?
Ergonomics is the science of fitting workplace conditions and job demands to workers’ capabilities. For example, the size data of human bodies to design chairs, tables, and walkways. While many people are adjusting to working from home, it is important to create an environment that is ergonomically friendly, especially for those who are sitting at a desk for long periods of time. Creating a proper ergonomic workspace is crucial to keep you comfortable at work and can prevent injuries from occurring overtime.
Creating the Perfect Ergonomic Workspace
Consider following these tips when creating a suitable workspace:
1. Choosing the right chair
- Adjust your chair’s height to make sure that your feet rest flat on the ground. Make sure that your hips, feet and elbows are bent at 90 degrees. Use a footrest to support your feet if needed. Armrests of your chair should be adjusted so that your arms can rest on them with ease, ensuring that your neck and shoulders are relaxed downwards.
2. Adjusting your desk and monitor height
- Position your computer monitor to the height of your eye level and at least an arm’s length away to reduce any strain on your neck or eyes. A good height would mean you shouldn’t have to hunch over or tilt your head up to see the computer screen. If you are using a laptop, adjust the height by using a laptop stand when typing to reduce strain and tension.
3. Organizing your desk space
- Keep frequently used tools within close proximity to minimize reaching. For instance, keep your keyboard mouse, pen and notepad, and telephone nearby to avoid repeatedly twisting to reach for these things. Make sure that there is clearance under your desk for your knees, thighs, and feet and try to not store items under your desk.
4. Having good posture
- To reduce strain, ensure your shoulders are relaxed and placed back. Align your head with your shoulders, and keep your hands at or below elbow level. Continue to be aware of your head position and posture throughout the day, as we often forget about our posture from concentrating on the computer too long.
5. Taking regular breaks and stretching
- Follow the 20-20-20 rule: After every 20 minutes of looking at your computer screen, give your eyes a 20 second break by looking at something else that is at least 20 feet away. Sitting at a desk for long periods of time can cause tight muscles and long-time compromise for pain in your back and neck. It’s crucial to remember to take stretching breaks every 30 minutes to relieve some tension and avoid pain overtime. Below are some stretches you can follow. Alongside with stretching, take a few minutes to go on a short walk to get your body moving and reduce eyestrain from starring at a computer for a long time.

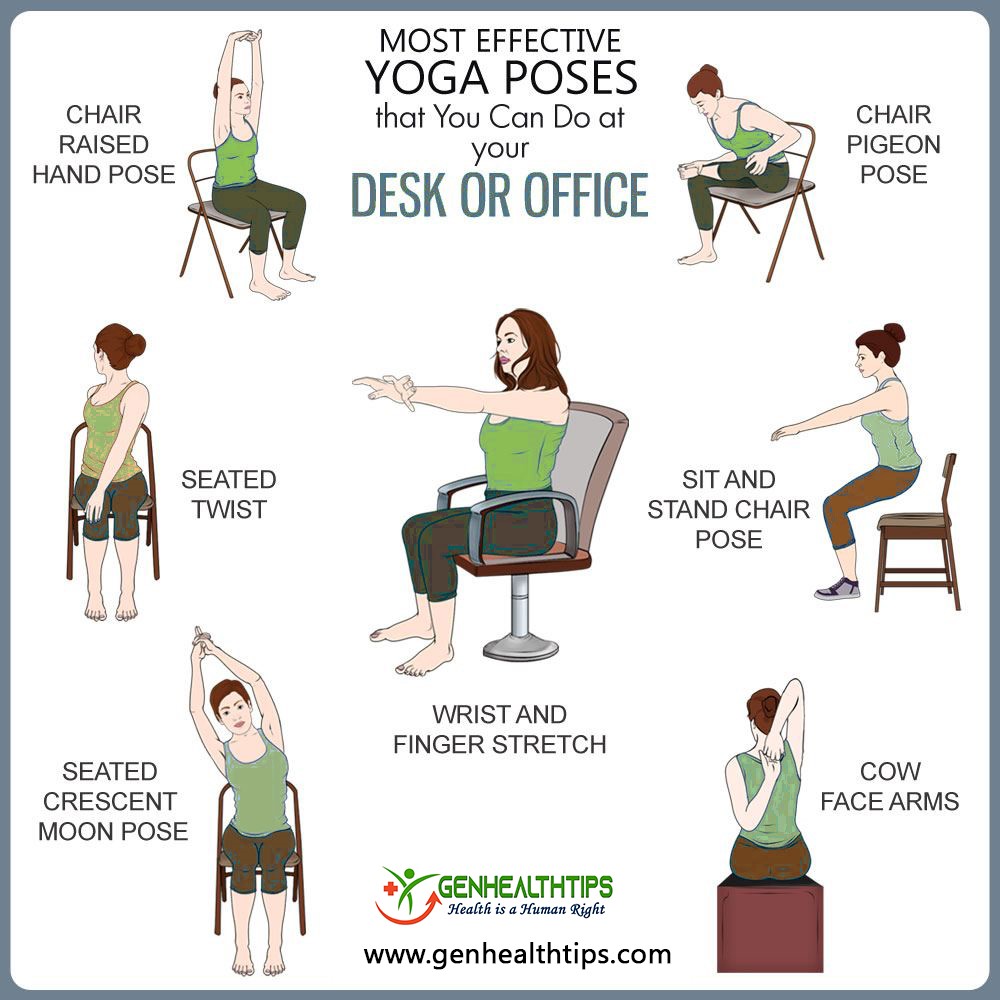
Proper Lifting
Posted on October 3, 2020 by admin
Why is the proper lifting technique important?
One of the most common causes of lower back injury is incorrect lifting technique. When you lift an object with bad posture, this causes a greater load to be placed through the bones, ligaments and discs in your spine which may lead to injury. Remember to use the correct body mechanics to lift safely and prevent back injury.
Before you lift, make sure to consider the following:
- Know the weight of the object – determine whether you are able to lift it on your own.
- Get help if the load is too heavy to carry on your own.
- Make sure your lift pathway is clear (check if the floor is wet/slippery, remove tripping hazards).
Lifting steps:
- Stand close to the object you will be lifting.
- Keep a wide stance – your feet should be shoulder width apart with one foot being slightly in front of the other to keep balance.
- Squat down when picking up the object by bending your knees and keeping your back straight. Bending your knees reduces the load that is created in your lower back, which can prevent back injuries from occurring.
- Lift the object slowly by using your arm and leg muscles rather than your back muscles and straightening your hips and knees. Breathe out as you lift. Remember to keep your back straight and do not twist while lifting!
- Hold the object as close to your body as possible. Hold the object near your abdomen region – do not hold the object above shoulder level.
- Pivot your feed by taking small steps to change directions. Do not twist your body.
- Bend your knees while slowly and carefully lowering the object to the new location.
- Cervical stenosis: In this condition, the narrowing occurs in the part of the spine in your neck.
- Lumbar stenosis: In this condition, the narrowing occurs in the part of the spine in your lower back. This is the most common form of spinal stenosis.
- Numbness or tingling in a hand, arm, foot or leg
- Weakness in a hand, arm, foot or leg
- Problems with walking and balance
- Neck pain
- In severe cases, bowel or bladder dysfunction (urinary urgency and incontinence)
- Numbness or tingling in a foot or leg
- Weakness in a foot or leg
- Pain or cramping in one or both legs when you stand for long periods of time or when you walk, which usually eases when you bend forward or sit
- Back pain
- Acute inflammatory phase – The first stage consists of the formation of blood clot within the damaged region.
- Proliferative phase – New blood vessels are formed while fibroblasts are recruited from circulation to produce new collagen.
- Tissue remodeling phase – The third stage starts after 3 weeks of the injury occurrence. During the wound healing process, there is a progressive maturation of collagen fibers in response to loads experienced by the ligaments. If force is applied in the wrong direction, there can be permanent damage of the ligaments.
- Calisthenics – Consists of a variety of movements that exercise large muscle groups, including push ups, sit ups, and running
- Weights – Strength training tools such as free weights, machines, kettle-bells, cables/pulleys
- Do exercises that involve all major muscle groups (chest, shoulders, back, hips, abdomen, arms)
- To improve good posture, select exercises that strengthen the trunk (abdomen)
- Never lift heavy weights alone (have a spotter)
- Warm up prior to high intensity exercises
- Use proper lifting techniques to prevent musculoskeletal injuries
- Exercise larger muscle groups before smaller ones (Ex. exercise legs before arms)

Spinal Stenosis
Posted on August 21, 2020 by admin
What is spinal stenosis?
Spinal stenosis, or narrowing of the spinal canal, is a condition that can squeeze sensitive spinal nerves. Some people with spinal stenosis may not have symptoms. Others may experience pain, tingling, numbness and muscle weakness. Symptoms can worsen over time.
The most common cause of spinal stenosis is osteoarthritis, the gradual wear and tear that happens to your joints as you age over time. Spinal stenosis is common in older adults because osteoarthritis begins to cause changes in most people’s spines by age 50.
The two main types of spinal stenosis are:
Symptoms
Cervical spine (in the neck):
Lumbar spine (in the lower back):
How can chiropractic treatment help with spinal stenosis?
Chiropractic treatment is an all-natural, non-invasive method of helping relieve painful symptoms as well as addressing spinal stenosis directly at the source. Chiropractic approaches spinal stenosis holistically; taking into account your symptoms, the current state of your spine, how your body is feeling, what makes your symptoms better or worse, and what you feel comfortable doing.
To diagnose spinal stenosis, your chiropractor may ask you about signs and symptoms, discuss your medical history, and conduct a physical examination. Then, they may order several imaging tests to help pinpoint the cause of your signs and symptoms. Imaging tests include, X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or CT scan. Spinal manipulation and other manual adjustments are the primary method of treatment.
Chiropractic treatment aims to widen the space available for the spinal cord within the spinal canal. By correcting the displacement of spinal discs, relieving tension held in tight muscles, and removing the pressure from spinal nerves, a patient with spinal stenosis can experience lessened symptoms. Chiropractic care is drastically less invasive than other treatment options such as injections, harmful medications, or open spine surgery.
If you’ve been suffering from spinal stenosis in either the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spine, or have felt symptoms that you believe can be spinal stenosis, contact us to book an appointment.
Tenosynovitis
Posted on August 5, 2020 by admin
Tenosynovitis is the inflammation of the fluid-filled sheath (called the synovium) that surrounds a tendon, typically leading to joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. The sheath of the tendon becomes thinner which is caused by the reduced lubrication between tendon and its sheaths due to the excess rubbing movements. Some secondary factors that increase the risk of tenosynovitis is having improper skill and posture when moving the wrist. The 2 common types of tenosynovitis are De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis and Trigger Finger Tenosynovitis.
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis:
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is a condition that affects the tendons in your wrist. Repeating a particular motion may irritate the sheath around the two tendons, causing thickening and swelling that restricts their movement. This condition affects tendons that abduct and extend the thumb necessary for dexterity and manipulation.
The exact cause of this type of tenosynovitis is unknown. However, any activity that requires repetitive hand or wrist movement can aggravate the condition – such as knitting, racket sports, lifting a baby, and walking a pet. Treatments for De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis include wearing a thumb splint to immobilize the thumb, preventing further abduction of the thumb.
Trigger Finger Tenosynovitis:
Trigger finger tenosynovitis is tenosynovitis of tendons that flex fingers. The cause of this condition occurs from repetitive and forceful flexing of fingers. As a result, one of the fingers gets stuck in the bent position due to the bulbous swelling that restricts finger flexion and may lock them in a fixed position. A bump, also known as a nodule, may occur from the inflammation of the tendon sheath. Trigger finger occurs mostly near metacarpophalangeal joints, middle and ring fingers of the dominant hand.
People whose work or hobbies require repetitive gripping actions are at higher risk of developing trigger finger tenosynovitis. Additionally, those with health problems such as rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes are at higher risk.
Ligaments and Tendons
Posted on May 13, 2020 by admin
Tendons and ligaments are fibrous bands of connective tissue that help stabilize body structures and facilitate body movements. The main difference between tendons and ligaments is that they connect different parts of the anatomy. Tendons connect muscles to bones, while ligaments connect bones to other bones.
Ligaments and tendons are made of 2 types of protein fibers: collagen and elastin. Collagen fibers have a small deformation range and high strength. Since collagen has such a high strength, they require more force to break down. Contrarily, elastin fibers have a large deformation range with low strength, meaning they are very weak and can break more easily. Ligaments such as the neck and wrists have more motion and movement because they consist of more elastin and less collagen.
Ligaments and Tendon Injury:
Repetitive motions with inadequate recovery periods are the cause of occupational ligament and tendon injuries due to the constant loading and unloading of force with no rest. Loading is the process of physical stresses acting on the body or on anatomical structures within the body.
A ligament injury occurs during the chronic process of loading and unloading, the tissue becomes longer and more fragile and eventually a small amount of force can easily fracture. In addition, cumulative loading can result in a decrease in bone density which increases the vulnerability of a ligament or tendon getting injured. An example of constant loading is by having improper posture for long periods of time which eventually leads to lower back injury.
Stages of Ligament Healing:
Resistance Training
Posted on May 7, 2020 by admin
Resistance training, also known as strength training, is a form of exercise that improves muscular strength and endurance. During a resistance training workout, you move your limbs against resistance provided by your body weight, gravity, bands, weighted bars or dumbbells. Resistance training is recommended to be exercised 2 times in a week. Exercises should be individualized depending on the individual’s knowledge on how to do specific exercises. Kinesiologists specialize in designing exercise programs for patients that need help overcoming chronic injuries and pain.

Types of Resistance Training:
Benefits of Resistance Training:
Resistance training can increase tensile strength of connective tissues – helping to strengthen tendons, muscle, and ligaments. It allows tissue to generate more tension and which makes them more resistant to injury. Strength exercises can contribute to optimal performance in daily activities, as it improves posture, encourages weight loss and maintenance, and lowers injury risk. Strength training also reduces the need to do more cardiovascular activities because it helps control blood sugar.
This type of training can also be extremely beneficial for older adults because it improves mobility and functional independence. Implementing resistance training in your physical activity can help in the long run by delaying bone diseases such as osteoporosis – a condition where bones lose their mineral content/bone density and become more vulnerable to fracture. Bone density is improved when stress is put on bones by doing resistance exercises.
Guidelines for Resistance Training:
Shockwave Therapy – Accelerate Healing Process
Posted on February 26, 2020 by admin
A shockwave is an intense, short energy wave that travels faster than sound. By introducing these high-energy waves into the body, shockwave therapy can speed up the healing process through stimulating the metabolism and enhancing blood circulation. These processes help regenerate damaged tissues at the injured areas. When human body fails to heal itself on its own, shockwave therapy could be a great solution.
Why Shockwave Therapy?
Shockwave therapy is an affordable non-surgical procedure that effectively speeds up the healing process after 1 to 2 treatments. Each treatment is rather short, usually takes 20 to 30 minutes. It is effective on treating many conditions such as calcific rotator cuff tendintis, plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendinopathy, scar tissue treatment, tennis elbow, jumper’s knee, stress fractures and non-healing ulcers.
The Procedures
Chiropractors will precisely locate the area to be treated by palpation. Then, sufficient amount of gel will be applied to the area for efficient and smooth transfer of the sound wave. The shockwave applicator will be slightly pushed against your skin, and the sound waves will be fired.
Here’s a link to a video illustrating the process of the treatment: https://youtu.be/rXj6ugQuYps
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Posted on January 16, 2020 by admin
MRI is a technique that uses magnetic field and computer-generated sound waves to obtain detailed images of organs and tissues in our body. The magnetic field inside the MRI machine temporarily realigns water molecules in your body. The aligned molecules produce faint signals with radio waves, and create cross-sectional MRI images. 3D images can be produced with MRI by viewing the organ or tissue in various angles.
This noninvasive imaging technique gives high-resolution images of our body tissues which helps identify different health issues. MRI is the most frequently used method to obtain images of the brain and spinal cord. Other common organs and tissues imaged with MRI include heart, blood vessels, internal organs (liver, kidney, pancreas etc.), bones and joints, as well as the breasts.
However, since MRI uses powerful magnets to generate a strong magnetic field, any presence of metal in your body can be attracted to the magnet and can be a safety hazard. Metal can also distort the MRI image. Tattoos or permanent makeup might contain metal and might affect the MRI result. Report to the doctor if you are pregnant or breast-feeding, as the effects of the contrast material that has to be injected are still not well understood.
Patellar Tendonitis
Posted on January 9, 2020 by admin
Patellar tendonitis, also known as jumper’s knee, is the inflammation of the patellar tendon, which connects your knee cap to your shin bone. This condition can weaken the connective tissue and can possibly lead to tears in your tendon. Possible causes of the inflammation of the patellar tendon include practicing repetitive movements, overusing the tendon or adding too much pressure to your tendon repeatedly.
Knee pain is one of the most common symptoms of patellar tendonitis. If you feel pain especially when jumping, running, stretching and bending your leg; tenderness or swelling at the lower part of your knee cap, it is likely that your patellar tendon is inflame. Some symptoms resemble other medical condition, X-ray is one of the best ways to diagnose patellar tendonitis.
Once diagnosed for patellar tendonitis, it is important to stop the activities that caused the problem until fully recovered. Other treatments such as applying ice packs to your knees helps reduce inflammation, and shockwave therapy speeds up the healing process.
