Chiropractic
Cauda Equina Syndrome
Posted on August 16, 2022 by Andrea Cheung
Introduction
Cauda equina is the collection of nerves at the very end of the spinal cord. When the cauda equina was damaged and compressed causing pain and numbness sensation, we call it “Cauda Equina Syndrome” (CES).
CES is very rare which only account for 1 in 2000 of lower back pain patients. However, if health practitioners failed to diagnosis CES, this will cause serious consequence to patient’s bladder, bowel, and sexual function.
Cause/Mechanism
The major cause of CES is a large lumbar disc herniation at immediate vicinity of L2 or below, which compresses the cauda equina. Infections such as meningitis can also lead to CES. Moreover, sacral fracture can also cause CES when it compresses the cauda equina.
Signs/Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of CES can be universal to other chronic disease. Common signs reported from patients are low back pain, unilateral or bilateral sciatica, motor weakness in lower extremities, and/or numbness around the buttock area. With regards to bladder and bowel dysfunction, it may not present in the early stage.
CES can be present acutely or chronically. With acute CES, patient may present sudden back pain with dramatic sensory changes around the buttock area, and possible weakness in urination. During chronic CES, previous symptoms mentioned will build up gradually or may fluctuate over weeks, months or even years. If the patient had slow onset of bladder and bowel dysfunction, it will present with increase severity and less responsive to management.
Health practitioners and patients should monitor the red flag to CES such as bladder dysfunction and numbness tingling between legs and around the anus if the patient have continuous back pain, sciatica, and increase urinary frequency and urgency.
Treatment
When patient has diagnosis with CES, surgery is the first option to prevent further neurological damage. Study had found significantly improvement in neurological outcome if patient had surgical operation within 24 hours of onset compare to 48 hours. Some patient may also be able to regain bladder continence if they have surgery within the 24 hours to 48 hours timeframe. Therefore, surgery should be done as soon as CES was diagnosed.
The goal of the surgery is to decompress any compressed lesions to improve sensory and motor deficits. However, some patient may still experience some degrees of neurological deficit.
References
Whiplash Associated Disorder
Posted on January 14, 2022 by Andrea Cheung
What is Whiplash Associated Disorder?
Whiplash is a general termed injury that usually take place in a motor vehicle crash where the head is subject to sudden acceleration and deceleration, causing forceful bending in neck region. Since the movement is unlikely to occur in normal human range of motion, the muscles that control your neck movement do not have time to respond to the force, causing damage to the neck region.
The Quebec Task Force classifies Whiplash into five gradings, based on severity:
- Grade 0: No complaint about pain, tenderness, or stiffness of the neck. No physical signs.
- Grade I: Complaint of pain, tenderness, or stiffness of the neck without physical signs.
- Grade II: Complaint of pain, tenderness, or stiffness of the neck with musculoskeletal signs such as decrease range of motion and point tenderness.
- Grade III: Complaint of pain, tenderness, or stiffness of the neck with neurological signs such as sensory deficits.
- Grade IV: Complaint of pain, tenderness, or stiffness of the neck with signs of fracture and dislocation.
Mechanisms
During a rear-end crush, the torso the carried forward, forcing the cervical spine, located in our neck, into an abnormal “S-shaped” position. Then, the head and neck were forced backwards since the torso was pulled forward during the collision. This may cause injuries to anterior cervical ligaments. The head and neck will swing forward as the driver stop the vehicle immediately.
Signs and symptoms
Whiplash Associated Disorder comprised range of symptoms including neck pain and stiffness, headache, memory loss, dizziness, dysphagia, and temporomandibular joint pain.
Clinical Diagnosis
Patients with history of sudden or excessive neck extension, flexion, or rotation are in the risk of whiplash injury. During initial assessment, patient may report having reduced cervical spine range of motion, loss of muscle control in both cervical spine and shoulder gridle, loss or decrease in balance and deficits in neck-influenced eye movement control. For more serious cases, some patient may experience muscle degeneration in the cervical extensor muscles, lead to long lasting pain and disability.
Treatment
In the first 96 hours after injured, mobilization such as active and passive range of motion exercises can result in reduced pain levels and improve function. Active rest, such as continue daily activity with brief rest period, can help blood flowing and muscle recover. Immobilization of long period of time can delay recovery time as muscle and ligament fibers are not aligned properly which can reduce strength and energy absorption capacity. Moreover, some patients will take NSAIDs to reduce inflammation, and neck rang of motion had reported improved after two weeks with medicine. Other physical treatments that practitioners will used are heat and cold packs, ultrasound therapy, and head traction. Theses can reduce pain and enhance recovery during the acute phase of whiplash injury.
During subacute phase, the goal for the patient is to return cervical muscle function as normal as possible. Light isometric and isotonic strengthening exercises that target the neck and scapular can help restore neck active range of motion. Light stretching also play a crucial role to improve tissue healing by increasing blood flow to the injured area. Vestibular and motor control exercises can improve neuro deficits and retraining muscle activation. Manual joint manipulation provided by chiropractors can reduce pain and initiate body’s natural healing processes. For ongoing management, continue with all the treatments stated above as well as increase the intensity of strengthen exercises.
References
Bannister, G., Amirfeyz, R., Kelley, S., & Gargan, M. (2009). Whiplash injury. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British Volume, 91-B(7), 845–850. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.91b7.22639
Barnsley, L., Lord, S., & Bogduk, N. (1994). Whiplash injury. Pain, 58(3), 283–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3959(94)90123-6
Elliott, J. M., Noteboom, J. T., Flynn, T. W., & Sterling, M. (2009). Characterization of Acute and Chronic Whiplash-Associated Disorders. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy, 39(5), 312–323. https://doi.org/10.2519/jospt.2009.2826
Pastakia, & Kumar, S. (2011). Acute whiplash associated disorders (WAD). Open Access Emergency Medicine, 29. https://doi.org/10.2147/oaem.s17853
Sterling, M. (2011). Whiplash-associated disorder: musculoskeletal pain and related clinical findings. Journal of Manual & Manipulative Therapy, 19(4), 194–200. https://doi.org/10.1179/106698111×13129729551949
Tameem, A., Kapur, S., & Mutagi, H. (2014). Whiplash injury. Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain, 14(4), 167–170. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjaceaccp/mkt052
Sciatica
Posted on by Andrea Cheung
What is sciatica?
Sciatica is the symptom of an underlying medical condition, not a medical diagnosis. However, this term has been incorrectly used to describe pain in back and leg symptoms by the general population. This is a term to describe a pain symptom that radiates from the middle or lower buttock down to the back and the side of the leg along the sciatic nerve, sometime it could radiate below the knees into the foot and toes. Sensory symptoms may also be reported by the patient. Usually, the pain only affects either left or right rather than both sides. Other thing to note is that Low back pain is not a consistent feature seen in sciatica but may also present in patient.
Symptoms and examination
Research has found that 90% of the cases are due to herniated disc that compress the nerve root from L4 to S1. Different levels of compression will present slightly different clinical features. With L4 compression, the pain is front and to the side of the thigh, which may sometimes mistake as a hip disease. Vis versa, L5 compression show pain at the back and the sides. Some other causes of sciatica might be lumbar canal or foraminal stenosis and tumors or cysts.
To examine whether a patient have sciatica, Straight Leg Raising Test have shown high sensitivity of 91%. When the patient is lying down and facing up, raising the whole leg straight can stretch the nerve root of the protruding disc. This will reproduce the pain and discomfort that the patient complains. If the leg is angled between 30 to 70 degrees with pain from buttock to below knee, disc compression of nerve root might be the cause of radiated pain.
Sometimes, sciatica might be mixed up with non-specific low back pain. Some major signs to justify sciatica are radiated pain towards foot or toes, numbness and paranesthesia.
Treatment
Conservative non-surgical treatments are recommended for patient. Most common initial treatment will be pain control by medication prescribed by family doctor, which could provide relief to patient’s discomfort. The most common medication is naproxen, used to relieve pain for various conditions. Other conservative treatment such as acupuncture, steroid injections, etc. might be beneficial but studies has been inconsistent with pain relief of sciatica. However, rest and bed rest are not recommended to reduce pain as it might lead to acute low back pain although it might provide instant relief. Staying active likely to be more beneficial in improving sciatica and aid in faster recovery.
Another conservative treatment is spinal manipulation. It is widely used to provide a short-term benefit in relief pain symptoms in addition to exercise program targeting the low back and hip. Study had found that patient who has sciatica of at least six weeks, both conservative and disc surgery might improve patient’s pain and function. But we must aware of possible confounding in the study due to self reported data and patients’ preference for treatment may also affect treatment outcome.
If pain does not diminish in six to eight weeks, patient should meet a neurologist, neurosurgeon, or orthopedic surgeon to discuss other treatment methods such as surgery. It is always the last resource to treat sciatica when practitioner suspect a disc herniation or disc rupture. However, evidence has shown controversial outcomes with surgery. Studies has shown patient who did surgery has faster relief of pain compare to conservative treatment.
Prevention
Exercise is always the best prevention protocols that a patient could do during their free time. Specific strengthening exercise that targets the core and the lower back can help protect the spine and maintain good posture. Patient can also stay active by jogging around the neighborhood or swimming and the pool.
Maintaining a good sitting posture is also important to prevent disc compression. Prevent bending the lower back which could reduce pressure on the discs and ligaments. Moreover, take a small break every 30 minutes of sitting can relief the pressure in the disc.
References:
Harvard Health Publishing. (2020, September 24). 5 tips with coping sciatica. https://www.health.harvard.edu/pain/5-tips-for-coping-with-sciatica
Koes, B. W., van Tulder, M. W., & Peul, W. C. (2007). Diagnosis and treatment of sciatica. BMJ, 334(7607), 1313–1317. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39223.428495.be
Ropper, A. H., & Zafonte, R. D. (2015). Sciatica. New England Journal of Medicine, 372(13), 1240–1248. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmra1410151
Valat, J. P., Genevay, S., Marty, M., Rozenberg, S., & Koes, B. (2010). Sciatica. Best Practice & Research Clinical Rheumatology, 24(2), 241–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2009.11.005
Ultrasound
Posted on October 28, 2021 by Andrea Cheung
What is ultrasound?
Ultrasound has been wildly accepted as a therapeutic modality among the medical field by delivering noninvasive soundwaves causing the molecules in our body to vibrate. Depends on the frequency that practitioner prescribed, it has slightly different positive effects to the patient. However, the main goal for ultrasound therapy is to decrease plain, enhance tissue repair, and aid in muscle relaxation.
What are the theories behind it?
The theory behind ultrasound therapy is the soundwaves transmitted by the machine will cause vibrations in deep tissues, thus heat production. Heat can enhance blood flow and reduce pain symptoms.
Usually, frequency range from 0.8MHz to 3MHz are used during the therapy session. Higher frequency will be used in deep tissues treatment since ultrasound energy will be absorbed by superficial tissues.
How does the treatment looks like?
Transducer can be applied directly to patient’s skin with a layer of gel moving in a circular motion or under water. However, direct application is more common in clinical settings. For acute injury, application will be around 3-5 minutes. For chronic injury, the treatment will take 5-10 minutes. Excessive exposure to ultrasound will cause burning to the skin and damage to cell tissues.
Is it safe? What are some contraindications?
Ultrasound therapy is generally safe for most people. However, certain conditions may prohibit patients from receiving ultrasound therapy. People who are pregnant and in the presence of a pacemaker should avoid direct application over the affected area. Moreover, application will not be placed in areas with cancer, fractures, or directly over spinal cord, and epiphyseal growth center.
Conclusion
Ultrasound therapy is very useful to treat pain symptoms and enhance tissue healing. In addition, incorporating exercise therapy such as active rehabilitation can enhance one’s physical function and recover quicker than only with electrical therapy.
Cause of Different Types of Back Pain
Posted on February 10, 2021 by George Wang
Lower back pain is common among population. Prior to treatment by health care professionals, it is useful to have an understanding on different diagnostic categories of lumbar discs terminology.
Normal
Defines discs that are morphologically normal, without the consideration of the clinical context and not inclusive of degenerative, developmental, or adaptive changes that could be considered clinically normal (Fardon, Williams, Dohring, Murtagh, Rothman & Sze, 2014, p.3).
Congenital/developmental variation
Includes discs that are congenitally abnormal or that have undergone changes in their morphology as an adaptation of abnormal growth of the spine, such as from scoliosis or spondylolisthesis (Fardon, Williams, Dohring, Murtagh, Rothman & Sze, 2014, p.3).
Degeneration
Includes subcategories of annular fissure, degeneration, and herniation
Annular fissure refers to separations between the annular fibers or separation of annular fibers from their attachments to the vertebral bone (Fardon, Williams, Dohring, Murtagh, Rothman & Sze, 2014, p.3).
Degeneration refers to all of the following: desiccation, fibrosis, narrowing of the disc space, diffuse bulging of the annulus beyond the dis space, fissuring, mucinous degeneration of the annulus, intradiscal gas, osteophytes of the vertebrae apophyses, defects, inflammatory changes, and sclerosis of the end plates (Fardon, Williams, Dohring, Murtagh, Rothman & Sze, 2014, p.4)
Herniation refers to a localized r focal displacement f disc material beyond the limits of the intervertebral disc space. The disc material may be nucleus, cartilage, fragmented apophyseal bone, annular tissue, or any combination thereof (Fardon, Williams, Dohring, Murtagh, Rothman & Sze, 2014, p.4).
Herniated disc may be classified as protrusion or extrusion, contained or uncontained (Fardon, Williams, Dohring, Murtagh, Rothman & Sze, 2014, p.5-6).
- Protrusion is present if the greatest distance between the edges of the dis material presenting outside the disc space is less than the distance between the edges of the base of that disc material extending outside the disc space
- Extrusion is present when, in at least one plane, any one distance between the edges of disc material beyond the disc space is greater than the distance between the edges of the base of the disc materials beyond the disc space or when no continuity exists beyond the disc space and that within the disc space
- Contained refers to if the displaced portion is covered by outer annulus fibers and/or the posterior longitudinal ligament;
- Uncontained when absent of such covering
Trauma
Includes disruption of the disc associated with physical and/or imaging evidence of violent fracture and/or dislocation and does not include repetitive injury, contribution of less than violent trauma to the degenerative process, fragmentation of the ring apophysis in conjunction with disc herniation, or disc abnormalities in association with degenerative subluxations (Fardon, Williams, Dohring, Murtagh, Rothman & Sze, 2014, p.6-7).
Inflammation/infection
Includes infections, infection-like inflammatory discitis, and inflammatory response to spondyloarthropathy. Includes inflammatory spondylitis of subchondral end plate and bone marrow manifested by Modic Type I MRI changes and usually associated with degenerative pathological changes in the discs (Fardon, Williams, Dohring, Murtagh, Rothman & Sze, 2014, p.7).
Neoplasia
Refer to primary or metastatic morphologic changes of disc tissues caused by malignancy (Fardon, Williams, Dohring, Murtagh, Rothman & Sze, 2014, p.7).
Miscellaneous paradiscal masses of uncertain origin
Refer to a paradiscal mass or an increase in the size of herniated disc material may be created by epidural bleeding and/or edema, unrelated to trauma or other known origin (Fardon, Williams, Dohring, Murtagh, Rothman & Sze, 2014, p.7).
Citation
Fardon, D. F., Williams, A. L., Dohring, E. J., Murtagh, F. R., Gabriel Rotheman, S. L., & Sze, G. K. (n.d.). Lumbar disc nomenclature: Version 2.0 Recommendations of the combined task forces of the North American Spine Society, the American Society of Spine Radiology and the American Society of Neuroradiology. The Spine Journal. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2014.04.022
Link to the article: https://ruperthealth.com/research/lumbardisc.pdf
Workspace Ergonomics
Posted on December 2, 2020 by admin
What is Ergonomics?
Ergonomics is the science of fitting workplace conditions and job demands to workers’ capabilities. For example, the size data of human bodies to design chairs, tables, and walkways. While many people are adjusting to working from home, it is important to create an environment that is ergonomically friendly, especially for those who are sitting at a desk for long periods of time. Creating a proper ergonomic workspace is crucial to keep you comfortable at work and can prevent injuries from occurring overtime.
Creating the Perfect Ergonomic Workspace
Consider following these tips when creating a suitable workspace:
1. Choosing the right chair
- Adjust your chair’s height to make sure that your feet rest flat on the ground. Make sure that your hips, feet and elbows are bent at 90 degrees. Use a footrest to support your feet if needed. Armrests of your chair should be adjusted so that your arms can rest on them with ease, ensuring that your neck and shoulders are relaxed downwards.
2. Adjusting your desk and monitor height
- Position your computer monitor to the height of your eye level and at least an arm’s length away to reduce any strain on your neck or eyes. A good height would mean you shouldn’t have to hunch over or tilt your head up to see the computer screen. If you are using a laptop, adjust the height by using a laptop stand when typing to reduce strain and tension.
3. Organizing your desk space
- Keep frequently used tools within close proximity to minimize reaching. For instance, keep your keyboard mouse, pen and notepad, and telephone nearby to avoid repeatedly twisting to reach for these things. Make sure that there is clearance under your desk for your knees, thighs, and feet and try to not store items under your desk.
4. Having good posture
- To reduce strain, ensure your shoulders are relaxed and placed back. Align your head with your shoulders, and keep your hands at or below elbow level. Continue to be aware of your head position and posture throughout the day, as we often forget about our posture from concentrating on the computer too long.
5. Taking regular breaks and stretching
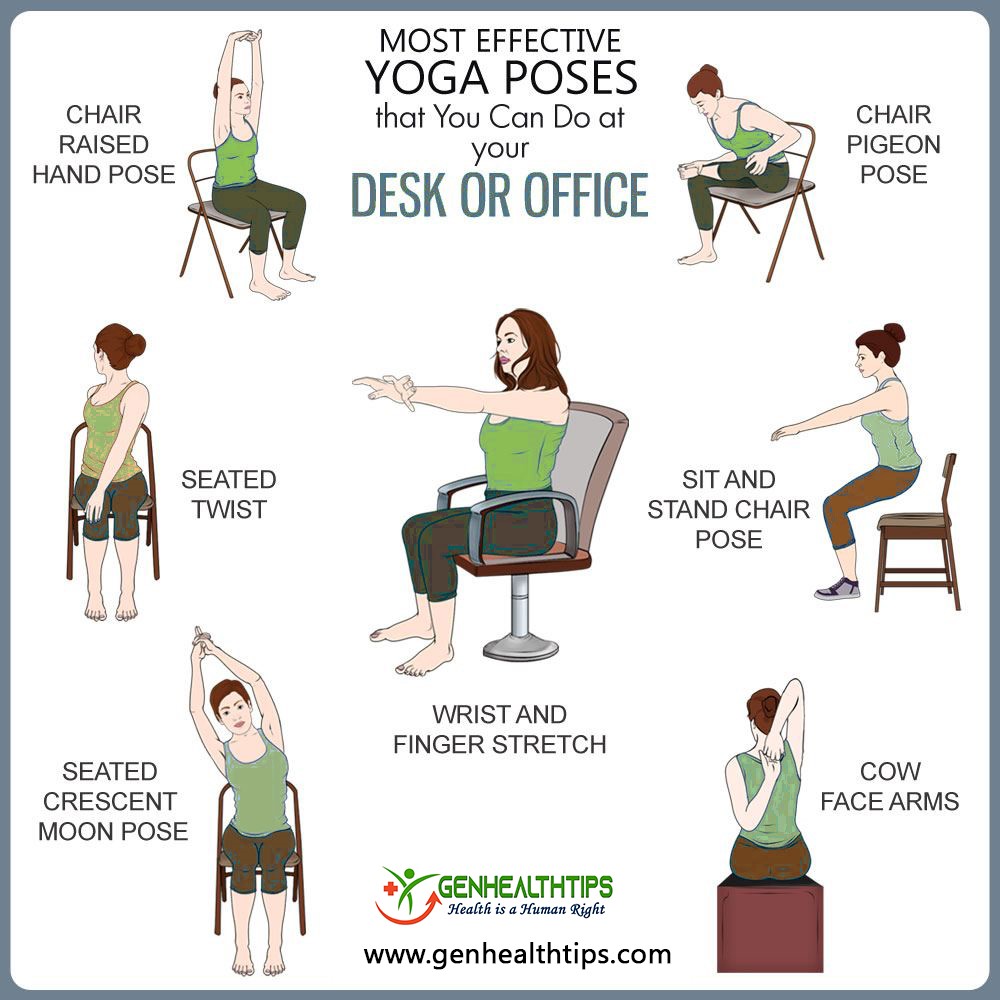
- Follow the 20-20-20 rule: After every 20 minutes of looking at your computer screen, give your eyes a 20 second break by looking at something else that is at least 20 feet away. Sitting at a desk for long periods of time can cause tight muscles and long-time compromise for pain in your back and neck. It’s crucial to remember to take stretching breaks every 30 minutes to relieve some tension and avoid pain overtime. Below are some stretches you can follow. Alongside with stretching, take a few minutes to go on a short walk to get your body moving and reduce eyestrain from starring at a computer for a long time.

Proper Lifting
Posted on October 3, 2020 by admin
Why is the proper lifting technique important?
One of the most common causes of lower back injury is incorrect lifting technique. When you lift an object with bad posture, this causes a greater load to be placed through the bones, ligaments and discs in your spine which may lead to injury. Remember to use the correct body mechanics to lift safely and prevent back injury.
Before you lift, make sure to consider the following:
- Know the weight of the object – determine whether you are able to lift it on your own.
- Get help if the load is too heavy to carry on your own.
- Make sure your lift pathway is clear (check if the floor is wet/slippery, remove tripping hazards).
Lifting steps:
- Stand close to the object you will be lifting.
- Keep a wide stance – your feet should be shoulder width apart with one foot being slightly in front of the other to keep balance.
- Squat down when picking up the object by bending your knees and keeping your back straight. Bending your knees reduces the load that is created in your lower back, which can prevent back injuries from occurring.
- Lift the object slowly by using your arm and leg muscles rather than your back muscles and straightening your hips and knees. Breathe out as you lift. Remember to keep your back straight and do not twist while lifting!
- Hold the object as close to your body as possible. Hold the object near your abdomen region – do not hold the object above shoulder level.
- Pivot your feed by taking small steps to change directions. Do not twist your body.
- Bend your knees while slowly and carefully lowering the object to the new location.
- Cervical stenosis: In this condition, the narrowing occurs in the part of the spine in your neck.
- Lumbar stenosis: In this condition, the narrowing occurs in the part of the spine in your lower back. This is the most common form of spinal stenosis.
- Numbness or tingling in a hand, arm, foot or leg
- Weakness in a hand, arm, foot or leg
- Problems with walking and balance
- Neck pain
- In severe cases, bowel or bladder dysfunction (urinary urgency and incontinence)
- Numbness or tingling in a foot or leg
- Weakness in a foot or leg
- Pain or cramping in one or both legs when you stand for long periods of time or when you walk, which usually eases when you bend forward or sit
- Back pain
- Acute inflammatory phase – The first stage consists of the formation of blood clot within the damaged region.
- Proliferative phase – New blood vessels are formed while fibroblasts are recruited from circulation to produce new collagen.
- Tissue remodeling phase – The third stage starts after 3 weeks of the injury occurrence. During the wound healing process, there is a progressive maturation of collagen fibers in response to loads experienced by the ligaments. If force is applied in the wrong direction, there can be permanent damage of the ligaments.

Spinal Stenosis
Posted on August 21, 2020 by admin
What is spinal stenosis?
Spinal stenosis, or narrowing of the spinal canal, is a condition that can squeeze sensitive spinal nerves. Some people with spinal stenosis may not have symptoms. Others may experience pain, tingling, numbness and muscle weakness. Symptoms can worsen over time.
The most common cause of spinal stenosis is osteoarthritis, the gradual wear and tear that happens to your joints as you age over time. Spinal stenosis is common in older adults because osteoarthritis begins to cause changes in most people’s spines by age 50.
The two main types of spinal stenosis are:
Symptoms
Cervical spine (in the neck):
Lumbar spine (in the lower back):
How can chiropractic treatment help with spinal stenosis?
Chiropractic treatment is an all-natural, non-invasive method of helping relieve painful symptoms as well as addressing spinal stenosis directly at the source. Chiropractic approaches spinal stenosis holistically; taking into account your symptoms, the current state of your spine, how your body is feeling, what makes your symptoms better or worse, and what you feel comfortable doing.
To diagnose spinal stenosis, your chiropractor may ask you about signs and symptoms, discuss your medical history, and conduct a physical examination. Then, they may order several imaging tests to help pinpoint the cause of your signs and symptoms. Imaging tests include, X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or CT scan. Spinal manipulation and other manual adjustments are the primary method of treatment.
Chiropractic treatment aims to widen the space available for the spinal cord within the spinal canal. By correcting the displacement of spinal discs, relieving tension held in tight muscles, and removing the pressure from spinal nerves, a patient with spinal stenosis can experience lessened symptoms. Chiropractic care is drastically less invasive than other treatment options such as injections, harmful medications, or open spine surgery.
If you’ve been suffering from spinal stenosis in either the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spine, or have felt symptoms that you believe can be spinal stenosis, contact us to book an appointment.
Tenosynovitis
Posted on August 5, 2020 by admin
Tenosynovitis is the inflammation of the fluid-filled sheath (called the synovium) that surrounds a tendon, typically leading to joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. The sheath of the tendon becomes thinner which is caused by the reduced lubrication between tendon and its sheaths due to the excess rubbing movements. Some secondary factors that increase the risk of tenosynovitis is having improper skill and posture when moving the wrist. The 2 common types of tenosynovitis are De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis and Trigger Finger Tenosynovitis.
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis:
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is a condition that affects the tendons in your wrist. Repeating a particular motion may irritate the sheath around the two tendons, causing thickening and swelling that restricts their movement. This condition affects tendons that abduct and extend the thumb necessary for dexterity and manipulation.
The exact cause of this type of tenosynovitis is unknown. However, any activity that requires repetitive hand or wrist movement can aggravate the condition – such as knitting, racket sports, lifting a baby, and walking a pet. Treatments for De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis include wearing a thumb splint to immobilize the thumb, preventing further abduction of the thumb.
Trigger Finger Tenosynovitis:
Trigger finger tenosynovitis is tenosynovitis of tendons that flex fingers. The cause of this condition occurs from repetitive and forceful flexing of fingers. As a result, one of the fingers gets stuck in the bent position due to the bulbous swelling that restricts finger flexion and may lock them in a fixed position. A bump, also known as a nodule, may occur from the inflammation of the tendon sheath. Trigger finger occurs mostly near metacarpophalangeal joints, middle and ring fingers of the dominant hand.
People whose work or hobbies require repetitive gripping actions are at higher risk of developing trigger finger tenosynovitis. Additionally, those with health problems such as rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes are at higher risk.
Ligaments and Tendons
Posted on May 13, 2020 by admin
Tendons and ligaments are fibrous bands of connective tissue that help stabilize body structures and facilitate body movements. The main difference between tendons and ligaments is that they connect different parts of the anatomy. Tendons connect muscles to bones, while ligaments connect bones to other bones.
Ligaments and tendons are made of 2 types of protein fibers: collagen and elastin. Collagen fibers have a small deformation range and high strength. Since collagen has such a high strength, they require more force to break down. Contrarily, elastin fibers have a large deformation range with low strength, meaning they are very weak and can break more easily. Ligaments such as the neck and wrists have more motion and movement because they consist of more elastin and less collagen.
Ligaments and Tendon Injury:
Repetitive motions with inadequate recovery periods are the cause of occupational ligament and tendon injuries due to the constant loading and unloading of force with no rest. Loading is the process of physical stresses acting on the body or on anatomical structures within the body.
A ligament injury occurs during the chronic process of loading and unloading, the tissue becomes longer and more fragile and eventually a small amount of force can easily fracture. In addition, cumulative loading can result in a decrease in bone density which increases the vulnerability of a ligament or tendon getting injured. An example of constant loading is by having improper posture for long periods of time which eventually leads to lower back injury.
Stages of Ligament Healing: